What is Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)?
Antimicrobial medicines destroy or slow the growth of microorganisms. They can be grouped according to the type of microorganisms they act against. For example, antibiotics are a specific type of antimicrobial medication that only act against bacteria, and not viruses or other microorganisms.
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) happens when microorganisms (such as bacteria, fungi and viruses) exposed to antimicrobial medicines undergo changes and prevent these medicines from working effectively. As a result, infections persist and increase risk of spread.
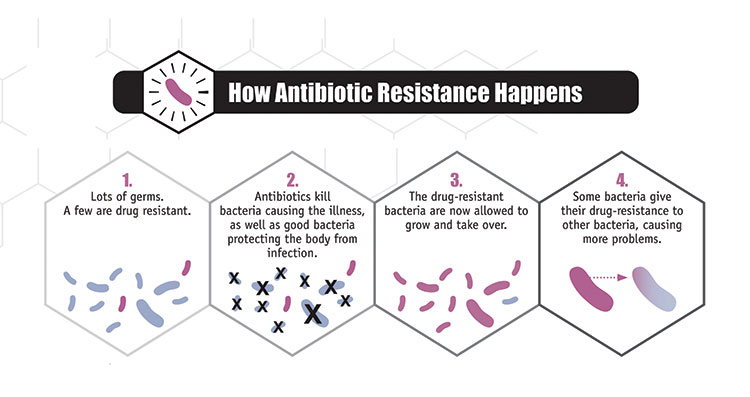
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Why is Antimicrobial Resistance a Concern?
With new resistance mechanisms emerging and spreading globally, AMR threatens the ability to prevent and treat an ever-increasing range of infections caused by bacteria, parasites, viruses and fungi. Without effective antimicrobials for prevention and treatment of infections, medical procedures (from transplants, diseases management to surgeries) become high risk. In turn, healthcare costs will increase as more intensive care for patients is required.
How does Antimicrobial Resistance Spread?
Antimicrobial resistance occurs naturally over time. However, it is worsened by the misuse and overuse of antimicrobials all around the world. Examples of misuse include when patients take antibiotics for viral infections like cold and flu, and when antibiotics are used to promote growth in animals.
Antimicrobial-resistant microorganisms are found in people, animals, food and the environment. They can be spread between people and animals, and from person to person. Improper food-handling, poor sanitary conditions and inadequate infection control measures encourage the spread of antimicrobial resistance.

Source: World Health Organisation
Watch a
video on Antimicrobial Resistance and learn more about the
Antimicrobial Resistance Coordinating Office.
What Can You Do to Fight Antimicrobial Resistance?
Preventing infection can reduce the risk of antibiotic use and limit the spread of antibiotic resistance. Take action to minimise the risk of infection through good hygiene practices, obtaining your necessary vaccinations and taking antibiotics responsibly.
Practice Good Hygiene Habits
 | Frequent Hand Washing
Our hands are in contact with germs that we are not able to see. Regular hand washing with soap is one of the easiest and most effective way to get rid of germs. Follow the hand washing steps below to ensure that your hands are clean. |
 |
Food Hygiene
Proper food handling and cooking can reduce the risk of infection by harmful microorganisms. The risk of foodborne illnesses can be mitigated by ensuring good hand hygiene, washing fruits and vegetables thoroughly before cooking, and cooking food thoroughly to eliminate harmful bacteria. |
 | Stay Home When Unwell Stay home, do not go to work or school if you are unwell. This helps to
prevent the spread of bacteria and viruses, and protect our community and our
loved ones. |
Get Vaccinated
 |
Protecting Yourself and Loved Ones
Are your vaccinations up to date? Several infectious diseases are preventable and vaccination strengthens your immunity against these diseases. Find out more about the recommended vaccines for your age group
here. |
Take Antibiotics Responsibly
Antibiotics, used to treat bacterial infections, are the most commonly-known class of antimicrobials. However, not all illnesses require antibiotics. For instance, antibiotics do not treat viral infections such as the cold, flu and most upper respiratory tract infections.
 | Follow Your Doctor's Advice
Using antibiotics inappropriately can lead to bacteria developing resistance. Only take antibiotics as they are prescribed and do not demand for antibiotics when your doctor says you do not
need them. Do not share your antibiotics with others. |
Antibiotic Tales Animated Video
Watch the animated snippet from "The Antibiotic Tales" comic book by Sonny Liew and Hsu Li Yang, to learn why antimicrobials are a precious resource and ways in which you can help to reduce the spread of antimicrobial resistance.